Modern enterprises rely on APIs to deliver connected digital experiences at speed. As API ecosystems expand, however, teams often struggle to access related data efficiently. Although APIs enable reuse, scalability, and API reuse across teams, fragmented access patterns slow development over time. Anypoint Datagraph solves this challenge by enabling a unified, graph-based approach to consuming data across multiple APIs in a single request.
A GraphQL Layer That Simplifies REST API Consumption
Rather than consuming REST APIs individually, Anypoint Datagraph introduces a GraphQL layer that unifies access to existing services. By doing so, it allows developers to interact with one endpoint instead of managing multiple API calls, while still supporting consistent API reuse across the organization.

As illustrated, Anypoint Datagraph sits above REST APIs and exposes them through GraphQL. Developers query the graph, while Datagraph retrieves and assembles data behind the scenes. As a result, teams eliminate the need for custom aggregation APIs and complex orchestration logic. At the same time, existing APIs remain unchanged, which preserves current investments and strengthens long-term API reuse.
How API Reuse Has Evolved Over Time
API usage patterns have changed significantly as organizations mature their integration strategies. While early approaches relied heavily on custom code, modern architectures emphasize reuse and self-service. Even so, many teams still face inefficiencies when working across multiple APIs, limiting effective API reuse at scale.
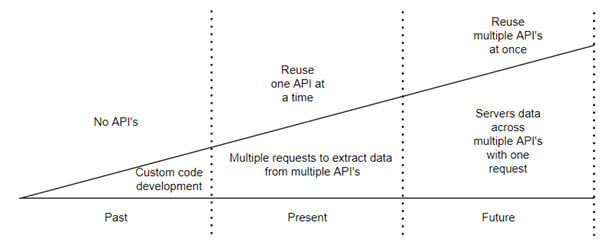
The image highlights this progression clearly. In the past, teams built custom code without APIs. Later, they began reusing APIs, although only one at a time, which required multiple requests to assemble data. Now, organizations aim to reuse multiple APIs simultaneously. Anypoint Datagraph enables this future state by serving data from several APIs through a single request, thereby reducing complexity and improving delivery speed while maximizing API reuse.
Visualizing API Relationships as a Unified Data Graph
Enterprise APIs typically align to individual systems such as orders, customers, invoices, products, and shipments. Although these APIs share logical relationships, consumers usually access them independently, which limits seamless API reuse across domains.
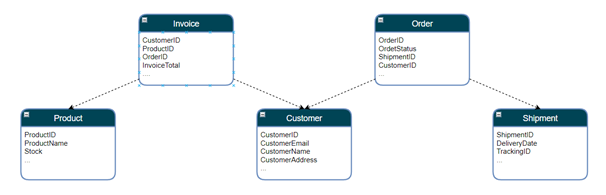
This diagram shows how entities connect through shared identifiers like CustomerID, OrderID, and ProductID. Anypoint Datagraph uses these relationships to build a unified data graph. Consequently, developers can traverse related data naturally without making multiple API calls. Instead of stitching responses together manually, they query the graph once and receive a consolidated response that improves API reuse without added complexity.
Faster Delivery Through a Unified API Schema
By defining relationships across APIs, Datagraph creates a unified schema that represents enterprise data as a connected graph. Because of this approach, developers can request only the fields they need while navigating relationships seamlessly, supporting efficient API reuse across channels and use cases. For example, a single query can retrieve invoice details alongside customer information, product data, and shipment status. This capability significantly reduces development effort while improving clarity and maintainability.
Clear Benefits for Development and Platform Teams
Organizations adopting Anypoint Datagraph gain tangible benefits across teams. Developers spend less time writing orchestration logic and more time building business features, supported by stronger API reuse patterns. Meanwhile, platform teams manage fewer APIs, which simplifies security and governance. Additionally, since Datagraph runs as a SaaS service, teams avoid runtime maintenance and patching overhead, thereby lowering operational costs.
Summary
Anypoint Datagraph enhances existing REST APIs rather than replacing them. By layering GraphQL on top of current services and exposing enterprise data as a unified graph, it enables a more efficient and scalable way to consume API data. As a result, organizations reduce complexity, accelerate delivery, and enable sustainable API reuse as their ecosystems continue to grow.